How to Rank Priority Organic Chemistry
Organic Chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that deals with carbon compounds. To learn the basics of the subject candidates must go through the NCERT books thoroughly.
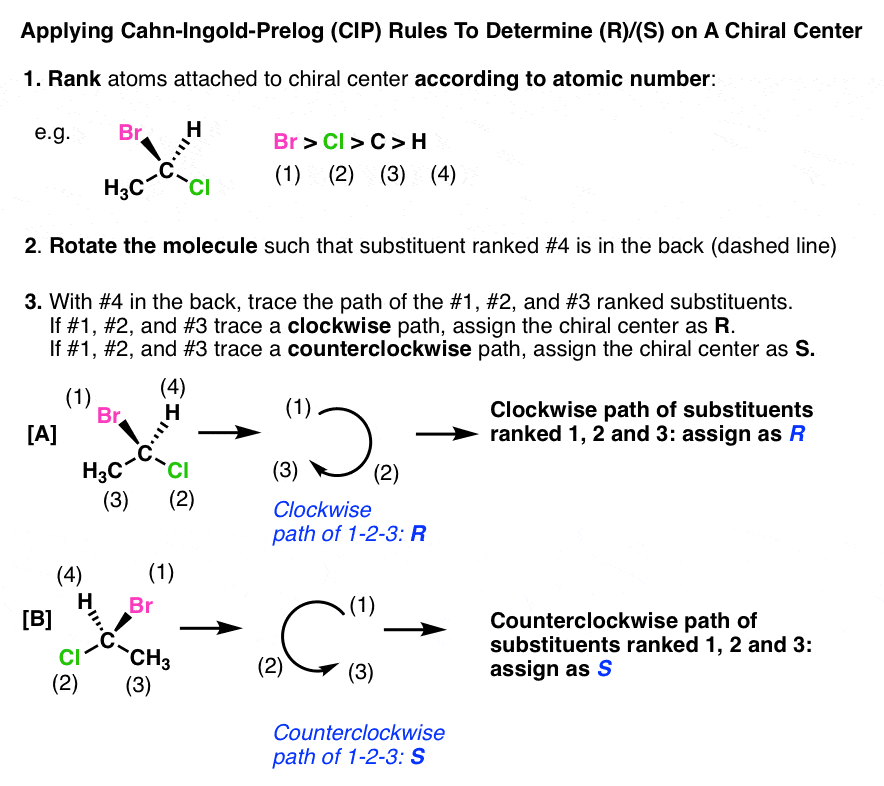
Introduction To Assigning R And S The Cahn Ingold Prelog Rules
Priority is assigned numerically with 1 being the highest priority 2 being next etc.

. I have added the principle in below after this 3 points After ranking the molecules according to Cahn Ingold Prelog principle then orient the molecule such that the lowest priority group is directed away from you. Identify and number the substituents. Because the terminal carbon is considered as being equivalently bonded to CCH while the methyl groups are all HHH.
Remember there must be as many numbers as there as substitutents. The priority group gets the suffix ending and the OH can be named with the prefix hydroxy-. CH3 CH CH2 CH3 OH 1 2 3 4 Butan-2-ol H3C CH C O OH OH 2-hydroxypropanoic acid If there are two or more -OH groups then di tri are HO CH2CH2 OH used.
Rank them according to decreasing atomic number. This video shows you how to prioritize substituents to find R and S configurations. 26 The purpose of the CIP system is to.
H3C H CH3 Cl 1 6 6 17 H3C H Cl CH3 1 6 6 17 high. Number the four atoms or groups of atoms such that 1 has the highest priority and 4 has the lowest priority. Give each atom connected to the chiral center a priority based on its atomic number.
The four atoms or groups attached to the chiral carbon are ranked in order of priority priority is decided by following sequence rules. Important to note that the additional Ns on CN are phantom. Jul 30 2018 at 2028.
Assigning Group Priorities- The Cahn Ingold Prelog rules. When we study about acidity of compounds we have to look their reactions with following compounds and products and then observe reaction rates. Functional group with a higher priority.
A molecule may contain any number of stereocenters and any number of double bonds and each gives rise to two possible configurations. Also Know what is priority in organic chemistry. The higher the atomic number the higher the priority.
Group 1 is highest priority group 4 is lowest priority 1 4 2 3 1 3 2 c l o c k w i s e 3R 1 4 2 1 2 3 an t i -c l o c k w i s e S For example in -glyceraldehyde the order of priority of the groups is OH CHO CH 2 OH H and the configuration is R. Feel free to ask questions in the comments below. Check Preparation Tips Tricks Important Topics and Formulas.
Most of the acidic organic compounds are weak acidsDissociation constant of acids K a value tells us about the acidity or strength of the acidWhen Ka value is high acidic strength is high. So based on this bromine gets priority one the oxygen gets priority two the methyl carbon is the third and the hydrogen is the lowest priority-four. If two or more of the atoms that are bonded directly to the chiral center are the same then prioritize these groups based on the next set of atoms ie atoms adjacent to the directly-.
Finding the Absolute Configuration R and S comes as a result of ranking and order substituents specifically by noting the configuration of the top 3 groups. Add the e on to the stem name though. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions regardless of the size of the molecule it is a part of.
If the high priority atoms are on opposite sides of the double bond it is designated as E. The CahnIngoldPrelog CIP sequence rules named for organic chemists Robert Sidney Cahn Christopher Kelk Ingold and Vladimir Prelog alternatively termed the CIP priority rules system or conventions are a standard process used in organic chemistry to completely and unequivocally name a stereoisomer of a molecule. 3 - Acids and Bases Worksheet See all chapters.
The Cahn-Ingold- Prelog priority rules CIP system or CIP conventions are a set of rules used in organic chemistry to name the stereoisomers of a molecule. Order of Precedence of Functional Groups. Atom of higher priority is assigned no1 atom of least priority is assigned no4.
Br has highest atomic number so it gets number 1 2 nd will be given to carbon that attaches to oxygen oxygen has higher atomic number than hydrogen 3 rd will be given to carbon that is attached to two other carbon and 4 th to the methyl carbon. Look up the atomic numbers of each of the atoms bonded to the stereocenter carbon of interest. This short primer takes you through the steps required to assign priority to different groups in a molecule.
The three remaining groups then project. Priority of common atoms. Chiral carbons are identified as having 4 unique substituents.
CHO H CH 2 OH OH HO O H C H 2 -glyceraldehyde as drawn previously 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 c l o c k w i s e R. 1 First we assign the priority to atomgroup according to their atomic number. This is the first step in assigning the absolute.
Number the atoms in the parent chain beginning at the end nearer the first branch point. The atom with the highest number always receives the top priority number 1 in most cases and. I Br Cl S F O N C H If both high priority atoms are on the same side of the double bond it is designated Z.
In organic chemistry functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. A Atom of higher atomic number gets priority. Priority of common atoms.
Ranking Acidity - Organic Chemistry Video Clutch Prep. Look at the atoms directly attached to each carbon of the double bond. First you have to rank the molecules around the two chiral centres of tartaric acid according to Cahn Ingold Prelog principle.
Download the video lesson worksheet. R and S Configuration using Cahn Ingold Prelog Priority Rules. Rank them according to decreasing atomic number.
I Br Cl S F O N C H. Treat them with the same priority as N but compared to a real N it has lower priority. The purpose of the CIP system is to assign an R or S descriptor to each.
If there is branching an equal distance from both ends then consider the next branch point repeat as required. In order to assign the stereochemistry of a stereocenter or double bond the priority or importance of the groups attached to the stereocenter or double bond must first be be determined. 1 - A Review of General Chemistry.
Number the higher the priority. NEET Organic Chemistry shares around 34 weightage of the total number of questions.
6 2 R S Sequence Rules Chemistry Libretexts

On What Basis Was The Priority Table Of The Iupac Nomenclature Of Organic Compounds Made Quora
What Is The Priority Rank Of Groups In Iupac Nomenclature Quora

Table Of Functional Group Priorities For Nomenclature Master Organic Chemistry

Table Of Functional Group Priorities For Nomenclature Master Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry Functional Groups Organic Chemistry Teaching Chemistry

R And S Configuration Using Cahn Ingold Prelog Priority Rules Leah Fisch Organic Chem Organic Chemistry Chemistry

R And S Configuration Using Cahn Ingold Prelog Priority Rules Leah Fisch Organic Chem Organic Chemistry Chemistry
8 7 Sequence Rules The E Z Designation Chemistry Libretexts
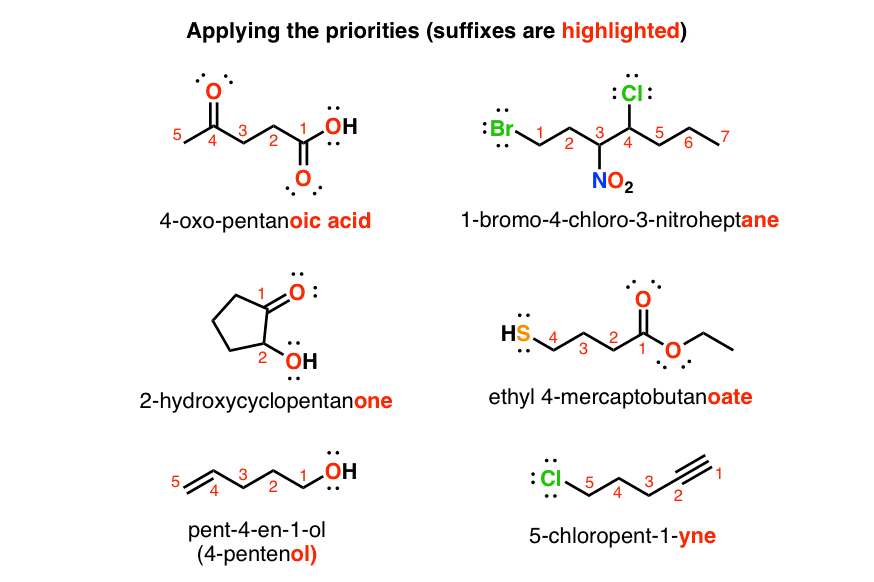
Table Of Functional Group Priorities For Nomenclature Master Organic Chemistry
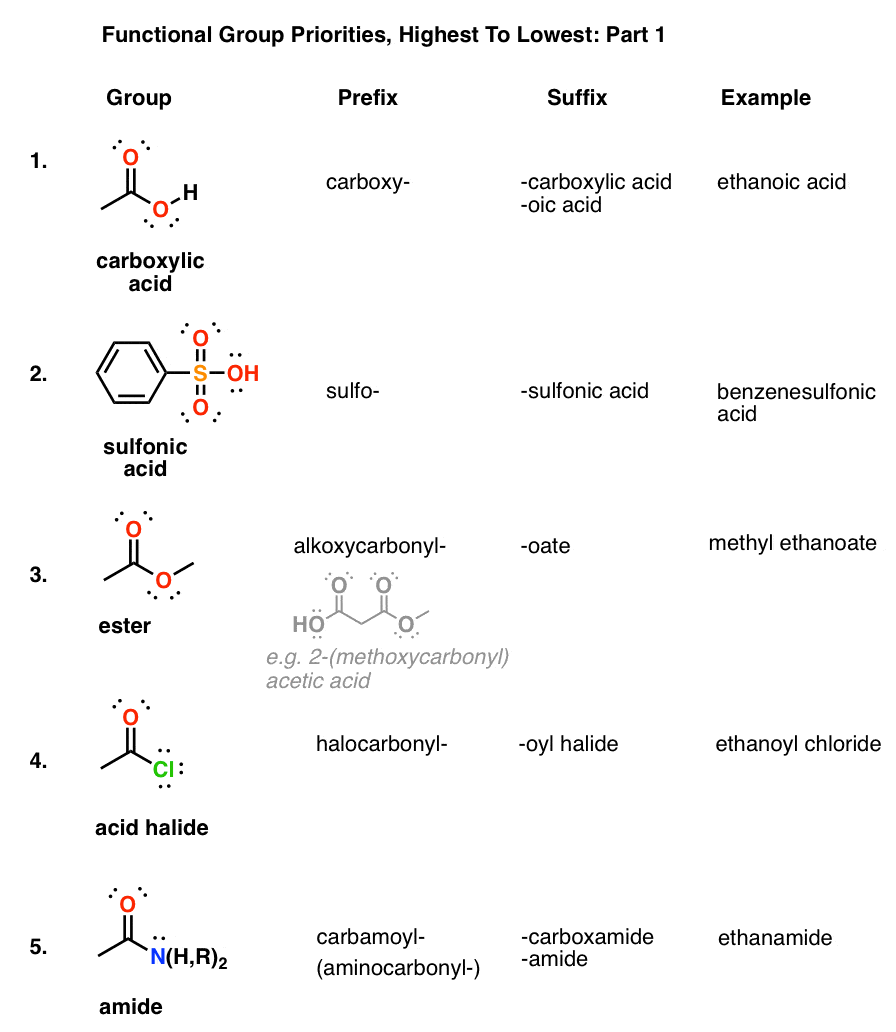
Table Of Functional Group Priorities For Nomenclature Master Organic Chemistry

Functional Group Priority Chart Organic Chemistry Cheat Sheet Organic Chemistry Study Teaching Chemistry Organic Chemistry Cheat Sheet

Ez Priority Rules Alkene Video Youtube

Rank The Folowing Substituent Groups In Order Of Decreasing Priority According To The Youtube
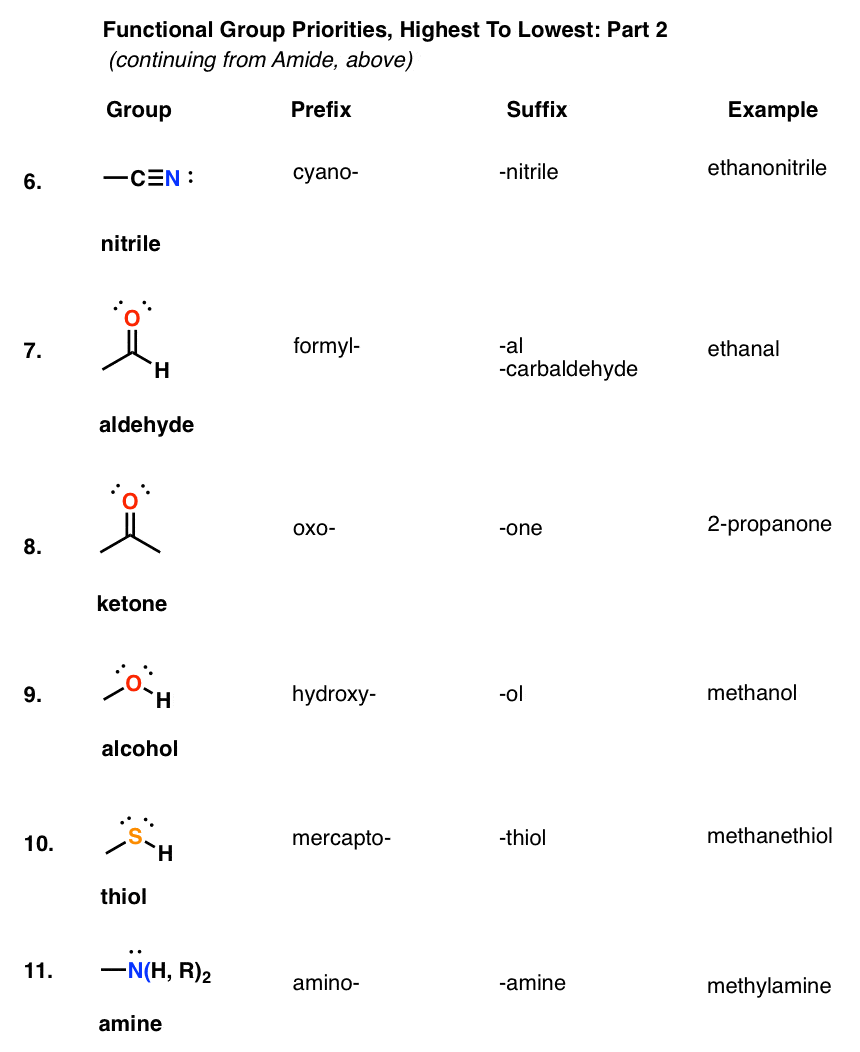
Table Of Functional Group Priorities For Nomenclature Master Organic Chemistry
Furman Chemistry 120 Organic Ranking Of Priority Of Functional Groups
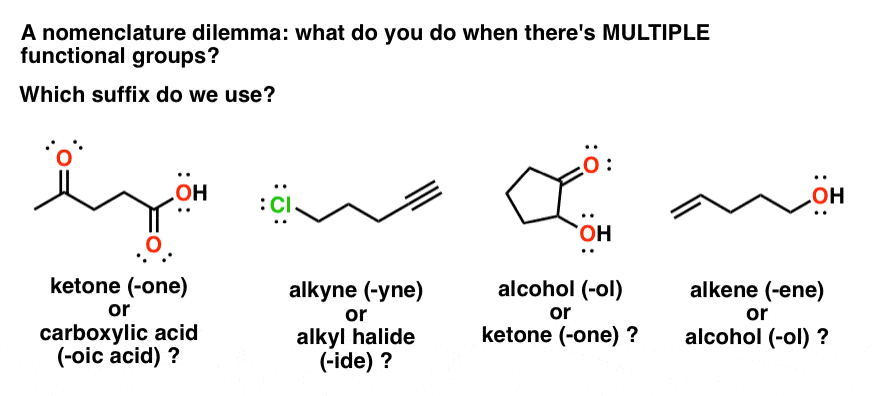
Table Of Functional Group Priorities For Nomenclature Master Organic Chemistry
6 2 R S Sequence Rules Chemistry Libretexts
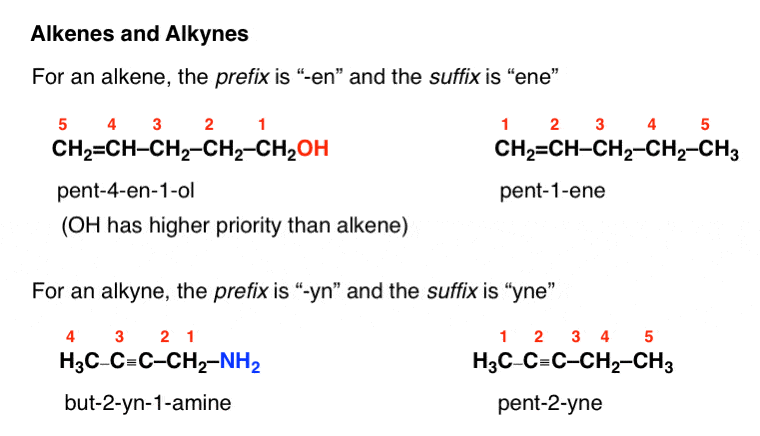
Table Of Functional Group Priorities For Nomenclature Master Organic Chemistry
